Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of cell theory and its implications.
- Analyze the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the processes of respiration and photosynthesis at the cellular and molecular levels and the relationship between them.
- Recognize how the structure of specialized cells relates to their different functions.
- Demonstrate knowledge of mitosis, meiosis, and the cell cycle.
- Demonstrate knowledge of active and passive transport across cell membranes.
- Recognize the structure and function of different biomolecules (e.g., lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids).
- Demonstrate knowledge of the role of enzymes as catalysts in cellular reactions and factors that affect enzyme function.
Sample Item:
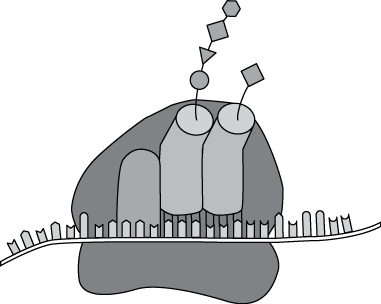
Along the strand, many shapes project up like teeth on a comb, each having either a concave or convex end. Above the center of the strand are three fingerlike units. The bottom of the leftmost unit appears to align with the strand, with three of the strand's projecting shapes in front of it. The bottom of each of the two units to the right is slightly above the strand's projections and has three tooth-like units projecting down, matching the strand's projections, convex to concave and concave to convex. Each of these two units has a string projecting upwards from the top. The string on the left unit contains a series of shapes, circular, triangular, square, and hexagonal. The string on the right unit contains a triangular shape at the end.
The ribosome shown in the diagram above is engaged in which of the following activities?
- assembling a protein from amino acids that are bound to tRNA
- breaking down proteins by hydrolysis to recycle their constituents within the cell
- transcribing DNA from a chromosome during mitosis
- transferring proteins to a transport vesicle for transport through the outer membrane
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
A. This question requires the examinee to analyze the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Ribosomes are cellular organelles located in the cytoplasm that are composed of ribosomal RNA and proteins. Ribosomes synthesize proteins by using messenger RNA as a sequencing template to organize transfer RNA molecules that are attached to specific amino acids. As the transfer RNA is sequenced by the ribosome, the attached amino acids are linked together to form a particular protein.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the diversity of life and the taxonomic relationships among living organisms.
- Recognize characteristics of the reproduction, development, and life cycles of representative organisms.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the functions of specialized structures and systems in protists, plants, animals, and fungi.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the structures and functions of human body systems.
- Analyze how organisms obtain, use, and store matter and energy.
- Analyze how organisms maintain homeostasis and fight diseases.
- Demonstrate knowledge of viruses and prions.
Sample Item:
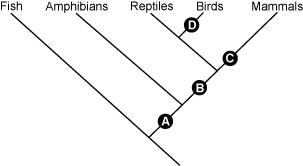
The first branch of the cladogram is labeled Fish. The Fish branch has one branch off it, labeled Mammals. There are two branches off Mammals. The first is labeled Amphibians, and the second is labeled Reptiles. The Reptiles branch has a branch off it labeled Birds. Four points are indicated. Point A lies on the Mammals branch between Fish and Amphibians. Point B lies on the Mammals branch between Amphibians and Reptiles. Point C lies on the Mammals branch between Reptiles and the Mammals label. Point D lies on the Birds branch.
The cladogram above depicts the evolution of vertebrate animals. Which point on the cladogram corresponds to the appearance of the amniote egg?
- point A
- point B
- point C
- point D
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
B. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the diversity of life and the taxonomic relationships among living organisms. The first amniotic egg evolved approximately 340 million years ago in ancestral reptiles during the Carboniferous period. These early reptiles were descended from amphibians and the evolution of the amniotic egg allowed reptiles to expand into drier terrestrial habitats. Reptiles, birds, and mammals all have amniotic eggs that are separate from the body of the mother and that can manage gas exchange, waste storage, and effectively store and transfer nutrients to the growing embryo. In order for the amniotic egg to be present in reptiles, birds, and mammals, it must have evolved in an early ancestor of the reptile, indicated as letter B in the cladogram shown.
Descriptive Statements:
- Apply the basic principles of heredity, Mendelian genetics, and the use of Punnett squares and the laws of probability.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the nature of the genetic code and the basic processes of DNA replication and protein synthesis.
- Recognize the methods and applications of genetic engineering.
- Analyze the principles and evidence of biological evolution to explain how species change over time.
- Demonstrate knowledge of major events in the history of life, mass extinctions, and the evolution of organisms, including humans.
Sample Item:
Which of the following statements best explains why mass extinctions, such as those that occurred at the end of the Permian and the end of the Cretaceous, are often followed by major adaptive radiations of the lineages that remain?
- Events thought to cause mass extinctions, such as asteroid or comet strikes or large-scale volcanic eruptions, can lead to higher mutation rates and rapid evolutionary change in surviving lineages.
- Surviving lineages are usually well adapted to occupy the changed environments and ecological conditions that have been brought about by the events causing the extinctions.
- Populations of surviving lineages are generally small and isolated and are more affected by genetic drift, natural selection, and other forces that cause rapid speciation and diversification.
- The life-forms filling most ecological niches have disappeared and the surviving lineages adapt and diversify to occupy these unoccupied niches with minimal competition.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
D. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of major events in the history of life, mass extinctions, and the evolution of organisms, including humans. Mass extinctions, such as occurred at the end of the Permian and the end of the Cretaceous, are triggered by catastrophic changes in Earth environments that eradicate large numbers of species. This environmental upheaval and dramatic loss in biological diversity eventually opens up many new habitats. The availability of unoccupied ecological niches and the minimal competition within those ecosystems supports extensive diversification of the surviving taxonomic groups. Species that survive a mass extinction for whatever reason become the bank for biological radiations that fill newly emptied and newly created ecological niches.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics of terrestrial and aquatic biomes, including representative species of plants and animals that inhabit them.
- Recognize strategies used by different organisms to obtain the basic needs for life.
- Analyze the relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers in a variety of ecosystems.
- Analyze the biotic and abiotic factors that affect population dynamics in ecosystems, including competition, resource availability, and habitat requirements.
- Analyze the cycling of matter and the flow of energy through different types of ecosystems.
- Recognize the ways both human activities and climate change affect ecosystems.
Sample Item:
The ecosystem around deep-ocean hydrothermal vents includes giant tube worms, several species of crustaceans, and a variety of other organisms. The primary source of nutrients and energy supporting this ecosystem is:
- bodies of dead phytoplankton and other organisms that continuously rain down from surface.
- mats of blue-green algae that colonize rocks surrounding the vents.
- zooplankton that move to the surface at night and back down to the vents during the day.
- bacteria that oxidize sulfur present in the outflow from the vents.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
D. This question requires the examinee to recognize strategies used by different organisms to obtain the basic needs for life. Although most life on Earth depends on sunlight, benthic organisms living in the lightless deep ocean rely on material that rains down into the benthos from higher in the water column. This light rain of organic debris, however, can only support extremely sparse populations of organisms on the deep-ocean floor. The extensive and dense biological communities found near deep-ocean hydrothermal vents are supported instead by chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria. The primary productivity of these chemosynthetic bacteria is based on the energy the bacteria derive from the oxidation of sulfur compounds in the mineral-rich water that flows from deep-sea hydrothermal vents and not from energy from the sun.